The Ultimate Guide to Exfoliation: Right Method for Your Skin

Anúncios
Achieving radiant skin often involves exfoliation, a process that removes dead skin cells, but selecting the proper method—physical or chemical—is crucial, as the best choice depends entirely on individual skin type and specific concerns to ensure optimal results and prevent irritation.
Embarking on the journey to healthier skin involves understanding its intricate needs, and among the myriad of skincare practices, The Ultimate Guide to Exfoliation: Choosing the Right Method for Your Skin’s Needs stands out as a fundamental pillar. This guide aims to demystify exfoliation, offering clarity on how to select the optimal technique for your unique skin profile, ensuring not just superficial glow but true skin vitality.
Anúncios
Understanding Exfoliation: Beyond the Surface
Exfoliation is far more than a simple step in a beauty routine; it’s a vital process that supports skin renewal and overall vitality. At its core, exfoliation involves the removal of dead skin cells from the outermost layer of the skin, the epidermis. This natural process slows down as we age, leading to a build-up of dull, flaky cells that can clog pores, diminish radiance, and even impede the absorption of other skincare products.
The accumulation of dead skin cells can result in a complexion that appears uneven in tone and texture, rough to the touch, and prone to breakouts. By regularly and appropriately exfoliating, we help our skin sheds these old cells, revealing the fresh, healthy skin beneath. This not only enhances the skin’s appearance but also allows serums, moisturizers, and treatments to penetrate more effectively, maximizing their benefits.
The Science Behind Skin Turnover
Our skin is constantly regenerating itself, a cycle known as cell turnover. New skin cells are formed in the deeper layers of the epidermis and gradually migrate to the surface. Once they reach the top, they are meant to naturally shed. However, factors such as age, environment, and specific skin conditions can disrupt this shedding process, causing dead cells to accumulate.
Anúncios
- Youthful Skin: In younger individuals, skin cell turnover typically occurs every 28-30 days, resulting in naturally smooth and radiant skin.
- Aging Skin: As we age, this cycle can extend significantly, sometimes taking 40-50 days or even longer, which contributes to a duller complexion and the appearance of fine lines.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to pollutants, harsh weather, and poor skincare habits can also hinder natural exfoliation.
Understanding the purpose of exfoliation helps in appreciating why it’s a non-negotiable step for many. It not only unveils brighter skin but also promotes a healthier skin barrier over time. Without proper exfoliation, skincare products might sit on the surface, offering minimal benefit. This fundamental understanding sets the stage for exploring the diverse methods available, ensuring that your approach is not just effective but also tailored to your skin’s unique needs.
Physical Exfoliation: The Power of Manual Renewal
Physical exfoliation, often referred to as mechanical exfoliation, is one of the most immediate ways to remove dead skin cells. This method involves the use of abrasive textures or tools to manually buff away the outer layer of the skin. It gives an instant sense of smoothness, making it a popular choice for those seeking immediate results and a tactile feeling of clean, refreshed skin.
The effectiveness of physical exfoliation lies in its direct action. Unlike chemical methods that work below the surface, physical exfoliants work purely on the epidermis, mechanically dislodging dead cells. Common forms include scrubs, brushes, and even microdermabrasion devices designed for home or professional use.
Scrubs: Granular Goodness (or Grit?)
When most people think of physical exfoliation, they envision facial or body scrubs. These products contain small, abrasive particles suspended in a cream or gel base. The particles manually polish the skin, sloughing off dead cells as they are massaged onto the surface.
There’s a wide variety of particles used in scrubs, ranging from natural ingredients like sugar, salt, and crushed nuts (such as apricot kernels) to synthetic microbeads (though these are largely phased out due to environmental concerns). The key to safe and effective scrub use lies in the particle size, shape, and frequency of application.
- Fine Grains: Ideal for more sensitive or delicate skin areas, as they provide a gentler abrasion.
- Rounded Particles: Less likely to cause micro-tears in the skin compared to irregularly shaped or jagged particles.
- Infrequent Use: Typically, scrubs should be used no more than 1-2 times per week to avoid over-exfoliation and irritation.
Brushes and Devices: Controlled Precision
Beyond scrubs, other physical exfoliation tools offer different levels of control and intensity. Facial brushes, both manual and electronic, provide a deeper cleanse and more uniform exfoliation than manual scrubbing with fingers. These brushes often have soft bristles designed to gently loosen and remove dead skin cells and impurities.
Microdermabrasion devices, which use fine crystals or a diamond tip to abrade the skin and vacuum up dead cells, offer a more intensive form of physical exfoliation. While professional microdermabrasion is common, at-home versions are also available, offering a controlled way to achieve smoother, brighter skin.
When considering physical exfoliation, it is paramount to prioritize gentleness. Aggressive scrubbing can lead to micro-tears in the skin, disrupting the skin barrier, and causing redness, irritation, or even worsening existing skin conditions like acne. For this reason, selecting products with finely milled, rounded particles and applying them with a light hand is crucial. Physical exfoliation, when done correctly, can significantly improve skin texture, clear pores, and enhance radiance, making it a valuable tool in a comprehensive skincare regimen for many.
Chemical Exfoliation: The Gentle Dissolving Act
Chemical exfoliation, while perhaps sounding intimidating, is often recommended as a gentler yet highly effective alternative to physical exfoliation for many skin types. Instead of relying on friction, chemical exfoliants use acids or enzymes to dissolve the bonds between dead skin cells, allowing them to slough away more easily. This method works by breaking down the “glue” that holds dead cells to the skin’s surface, promoting a smoother texture and brighter complexion without mechanical abrasion.
The beauty of chemical exfoliants lies in their ability to offer a more uniform and controlled exfoliation process, often reaching deeper into the pores than physical methods. This can be particularly beneficial for specific skin concerns, such as acne, hyperpigmentation, and fine lines, providing targeted treatment and long-term improvements in skin health.
AHAs: The Surface Smoothers
Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs) are water-soluble acids derived from sugary fruits. They work primarily on the skin’s surface, making them excellent for addressing concerns like uneven skin tone, rough texture, and superficial pigmentation. AHAs help to loosen the bonds between dead skin cells, promoting their shedding and revealing fresh, luminous skin beneath.
Common AHAs include:
- Glycolic Acid: Derived from sugar cane, it has the smallest molecule size, allowing for deeper penetration and more potent exfoliation. It’s often used for texture improvement, hyperpigmentation, and anti-aging.
- Lactic Acid: Derived from milk, it has a larger molecule size than glycolic acid, making it gentler and more hydrating. Ideal for sensitive or dry skin types.
- Mandelic Acid: Derived from bitter almonds, it has a significantly larger molecule and penetrates slowly, making it extremely gentle and suitable for very sensitive skin, rosacea, and even acne.
AHAs are versatile and can be found in various product forms, from cleansers and toners to serums and peels. Regular use can lead to improved skin clarity, reduced appearance of fine lines, and increased hydration.
BHAs: The Oil-Soluble Champions
Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs), most notably salicylic acid, are oil-soluble, which gives them a unique advantage: they can penetrate oil and therefore dive deep into pores. This characteristic makes BHAs exceptionally effective for treating oily, acne-prone, and congested skin.
Salicylic acid works by:
- Dissolving Sebum: It helps to break down excess oil and debris within the pores, preventing blockages that lead to blackheads, whiteheads, and acne.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: It possesses anti-inflammatory qualities, which can help calm redness and irritation associated with breakouts.
- Blackhead & Whitehead Treatment: Highly effective in clearing existing blemishes and preventing future ones by keeping pores clean.
BHAs are often found in acne treatments, cleansers, and toners. Their ability to purify pores makes them a cornerstone ingredient for anyone struggling with breakouts or excessive oiliness.
Enzymes: The Mildest Option
Enzymatic exfoliants, often derived from fruits like pineapple (bromelain) and papaya (papain), offer the mildest form of chemical exfoliation. They work by selectively breaking down keratin proteins in dead skin cells without affecting living cells. This makes them ideal for highly sensitive skin or for individuals who find AHAs and BHAs too strong.
Enzyme exfoliants provide a gentle brightening and smoothing effect, making them suitable for regular use without the risk of over-exfoliation. They are a great entry point into chemical exfoliation, offering a soft removal of dullness. Chemical exfoliation, when chosen thoughtfully based on skin type and concerns, can transform the skin, promoting a healthier, more vibrant complexion with consistent use.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Skin Type
Selecting the correct exfoliation method is paramount to achieving healthy, glowing skin without causing irritation or damage. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution; what works wonders for one person might be detrimental to another. The key is to understand your skin type and its specific needs, then match it to the most suitable exfoliation technique.
This careful consideration prevents common pitfalls like over-exfoliation, which can compromise the skin barrier leading to redness, sensitivity, and even breakouts. Instead, a tailored approach can lead to remarkable improvements in texture, tone, and overall skin health.
For Oily and Acne-Prone Skin
Oily and acne-prone skin types often benefit significantly from exfoliation due to excess sebum production and clogged pores.
The ideal choice here is typically Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs), specifically salicylic acid.
- Why BHAs? Their oil-soluble nature allows them to penetrate deeply into pores, dissolving sebum and dead skin cells that contribute to blackheads, whiteheads, and pimples. Salicylic acid also has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce the redness associated with acne.
- Frequency: Start with 2-3 times per week, gradually increasing if your skin tolerates it well. Daily use might be an option for some, but always observe your skin’s reaction.
- Avoid: Harsh physical scrubs with jagged particles, as these can spread bacteria and worsen inflammation.
For Dry and Sensitive Skin
Dry and sensitive skin requires a very gentle approach to exfoliation. Over-exfoliation can strip natural oils, leading to increased dryness, redness, and irritation.
Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs), particularly lactic acid, are often the best choice for these skin types.
- Why AHAs? Lactic acid has a larger molecular size and is also a humectant, meaning it helps attract and retain moisture. This makes it effective for gentle surface exfoliation without overly drying the skin. Mandelic acid is another excellent option for highly sensitive skin due to its very large molecule size and slow penetration.
- Frequency: Begin with once a week, and if well-tolerated, you might increase to twice a week. Enzymatic exfoliants are also a fantastic, very mild alternative for extremely sensitive skin.
- Avoid: Strong physical scrubs, high concentrations of glycolic acid, or BHAs, unless specifically prescribed by a dermatologist for a targeted issue.
For Combination Skin
Combination skin presents a unique challenge, with oily areas (T-zone) and dry or normal areas (cheeks). A balanced approach is crucial to address both concerns.
Consider a combination of gentle chemical and physical exfoliation, or targeted application.
- Targeted Chemical Exfoliation: Use a BHA product on oily T-zone areas, and a gentle AHA (like lactic acid) on drier areas.
- Gentle Physical & Enzyme: A very fine-grained scrub or an enzymatic exfoliant perhaps once a week universally can offer mild surface smoothing.
- Frequency: Alternate between methods, ensuring not to over-exfoliate any one area. For example, BHA two times a week on the T-zone, and an AHA once a week on other areas.
For Normal Skin
If you have normal skin, you generally have more flexibility in your exfoliation choices. The goal is to maintain skin health and prevent dullness.
Both AHAs and gentle physical exfoliation can be effective.
- Variety: You can experiment with different AHAs (glycolic or lactic acid) to see what your skin responds to best. Gentle physical scrubs with rounded beads or a facial brush can also be used.
- Frequency: 2-3 times per week, depending on factors like climate, age, and other skincare products you are using.
For Aging Skin
Aging skin often experiences slower cell turnover, making exfoliation particularly beneficial for stimulating renewal and improving the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
AHAs, especially glycolic acid, are highly effective.
- Why AHAs? Glycolic acid helps improve skin texture, reduces the appearance of fine lines, and promotes a more even skin tone. Regular exfoliation also allows anti-aging serums and treatments to penetrate more effectively.
- Consider Professional Treatments: For more significant concerns, professional peels (higher concentration AHAs or other acids) or microdermabrasion can offer deeper exfoliation and collagen stimulation.
- Frequency: 2-3 times per week with at-home products; professional treatments as advised by a specialist.
The journey to effective exfoliation begins with self-assessment. Understanding your skin’s unique characteristics and sensitivities is the first step toward selecting a method that truly enhances its health and radiance. Always start with lower concentrations and less frequent applications, gradually increasing as your skin adapts, and listen closely to what your skin tells you.
Beyond Basic Advice: Advanced Tips and Common Pitfalls
While choosing the right exfoliation method for your skin type is crucial, understanding the nuances of how and when to exfoliate, and being aware of common mistakes, can significantly enhance your results and safeguard your skin’s health. Exfoliation is a powerful tool, but like any powerful tool, it requires judicious use and a thoughtful approach.
Many enthusiastic exfoliators fall into the trap of “more is better,” which often leads to adverse reactions. Advanced tips focus on integration, product synergy, and protective measures.
Integrate Gradually and Observe
One of the most important pieces of advanced advice is to introduce new exfoliants gradually. Your skin needs time to adjust, especially to chemical exfoliants which can be quite potent.
- Start Low, Go Slow: Begin with a lower concentration of the active ingredient, and use it only once or twice a week.
- Patch Test: Before applying any new exfoliant to your entire face, perform a patch test on a small, inconspicuous area (like behind the ear or on your inner arm) to check for irritation or allergic reactions.
- Listen to Your Skin: Pay close attention to how your skin responds. Any persistent redness, itching, burning, or excessive dryness is a sign that you might be over-exfoliating or that the product is too strong for you.
Beware of Over-Exfoliation: The Enemy of Skin Health
Over-exfoliation is perhaps the most common pitfall. It occurs when you exfoliate too frequently, too aggressively, or use products that are too strong for your skin. The consequences can be detrimental to your skin’s barrier function.
Signs of over-exfoliation include:
- Shiny, “squeaky clean” feeling (this is a sign your natural oils have been stripped).
- Redness, inflammation, and increased sensitivity.
- Breakouts that are worse than usual, or new types of blemishes.
- Tiny bumps or rashes.
- Increased dryness, flakiness, or tightness.
If you suspect you’ve over-exfoliated, stop all exfoliating activities immediately. Focus on repairing your skin barrier with gentle, hydrating, and barrier-supporting products (e.g., ceramides, hyaluronic acid, soothing ingredients like centella asiatica). Sun protection is especially critical during this recovery period.
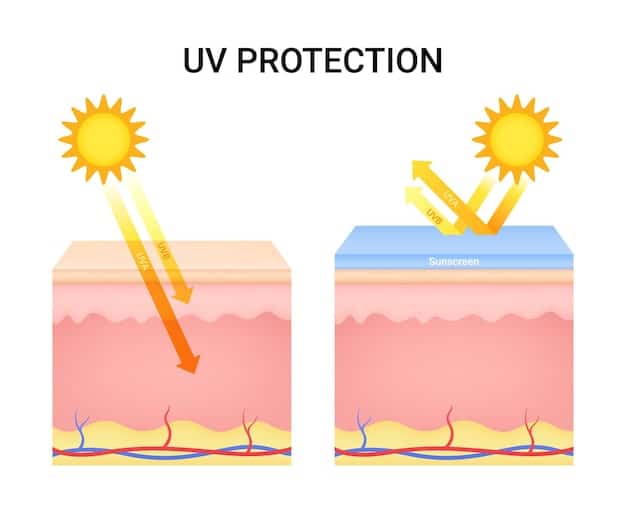
Sun Protection is Non-Negotiable
Exfoliation, particularly chemical exfoliation, can make your skin more susceptible to sun damage. This is because by removing the outer layers of dead skin, you expose newer, more vulnerable skin cells.
- Daily SPF: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher every single day, regardless of the weather or whether you’re indoors.
- Reapply: Reapply sunscreen every two hours when exposed to direct sunlight, or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
- Protective Measures: Consider wearing wide-brimmed hats and seeking shade, especially during peak sun hours.
Product Synergy and Layering
Be mindful of how your exfoliant interacts with other active ingredients in your routine. Combining too many potent actives can lead to irritation.
- Retinoids and Exfoliants: If you use retinoids (like tretinoin or retinol), introduce exfoliants with extreme caution and reduce frequency. It’s often recommended to alternate nights (e.g., retinoid one night, exfoliant the next, or use them on separate days).
- Vitamin C: While beneficial, some forms of Vitamin C (especially L-Ascorbic Acid) can be irritating when combined directly with strong exfoliants. It’s often best to use Vitamin C in the morning and exfoliants at night, or on alternating days.
- Hydration is Key: Always follow exfoliation with hydrating and moisturizing products to replenish the skin’s moisture barrier and soothe any potential irritation.
Advanced exfoliation is about balance and consistency. It’s not about how strong or how often you exfoliate, but how intelligently you integrate this step into a holistic skincare regimen, ensuring your skin remains healthy, resilient, and radiant. Always seek professional advice from a dermatologist if you have specific skin conditions or concerns.
Long-Term Benefits and Maintenance for Lasting Radiance
Exfoliation is not a one-time fix but a consistent practice that yields substantial long-term benefits for skin health and appearance. By regularly and appropriately removing dead skin cells, you’re not only revealing an immediate glow but also laying the groundwork for sustained radiance, improved product efficacy, and a resilient skin barrier. The true power of exfoliation is unlocked through careful maintenance and an understanding of its cumulative positive effects.
Consistent, mindful exfoliation contributes to a more youthful, even-toned, and clear complexion over time. It’s about creating a sustainable routine that supports your skin’s natural renewal process without causing stress or damage.
Enhanced Product Absorption and Efficacy
One of the most significant long-term benefits of regular exfoliation is its role in optimizing your entire skincare routine. When dead skin cells accumulate on the surface, they act as a physical barrier, preventing serums, moisturizers, and active treatments from properly penetrating the skin.
By regularly buffing away this superficial layer, you ensure that your expensive and carefully chosen skincare products can truly work their magic. Ingredients like hyaluronic acid, peptides, antioxidants, and retinoids can reach their intended targets more effectively, leading to:
- Deeper Hydration: Moisturizers penetrate better, keeping skin supple and plump.
- More Potent Treatments: Anti-aging serums and blemish treatments can deliver their active ingredients to where they are needed most.
- Improved Results: The overall efficacy of your skincare regimen is significantly boosted, leading to better outcomes for your skin concerns.
Stimulated Cell Turnover and Collagen Production
Beyond simply removing dead cells, exfoliation can also subtly stimulate the skin’s natural processes. Chemical exfoliants, particularly AHAs, have been shown to encourage cell turnover, prompting the skin to produce new, healthy cells more regularly. This accelerated renewal contributes to a fresher, more vibrant complexion.
Moreover, certain exfoliants like glycolic acid are believed to have a role in stimulating collagen production over time. Collagen is the protein responsible for skin’s firmness and elasticity. By supporting collagen synthesis, regular exfoliation can contribute to:
- Reduced Fine Lines and Wrinkles: A smoother appearance as skin plumps from within.
- Improved Skin Firmness: Helping to maintain a more youthful contour.
- Enhanced Skin Texture: A general refinement of the skin’s surface, making it feel softer and look more uniform.
Prevention of Breakouts and Congestion
For those prone to acne and breakouts, consistent exfoliation is a powerful preventative measure. By keeping pores clear of dead skin cells and excess sebum (especially with BHAs), you significantly reduce the likelihood of blockages that lead to blackheads, whiteheads, and inflamed pimples. This proactive approach helps maintain clear skin and fewer inflammatory lesions over time.
Maintaining a Balanced and Resilient Skin Barrier
While over-exfoliation can disrupt the skin barrier, appropriate and consistent exfoliation contributes to a healthier, more resilient one. By shedding old, damaged cells and promoting the growth of new ones, the skin’s natural barrier function is optimized. A strong skin barrier means better protection against environmental aggressors, reduced sensitivity, and improved ability to retain moisture.
Long-term maintenance involves vigilance. Continuously assess your skin’s needs, as they can change with seasons, age, and lifestyle. Adjust your exfoliation frequency and product choices accordingly. Remember that consistency, when balanced with gentleness, is the cornerstone of lasting skin radiance. Integrating proper post-exfoliation care—such as hydration and sun protection—solidifies these benefits, ensuring your skin remains healthy, luminous, and youthful for years to come.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| ✨ Skin Renewal | Exfoliation removes dead skin cells, promoting cell turnover for brighter skin. |
| 🔬 Method Match | Match exfoliation method (physical/chemical) to your specific skin type and concerns. |
| 🚫 Avoid Over-Exfoliation | Excessive exfoliation can damage skin barrier; signs include redness and sensitivity. |
| ☀️ Sun Protection | Always use broad-spectrum SPF 30+ daily, as exfoliated skin is more sun-sensitive. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Exfoliation
The ideal frequency depends on your skin type and the method used. Generally, 1-3 times a week is recommended. Sensitive skin might only tolerate once a week, while oilier skin types could handle 2-3 times. Always start with less frequent application to assess your skin’s tolerance and avoid over-exfoliation.
While some people with resilient skin might alternate, it’s generally best to choose one primary method to avoid over-exfoliation. If you do use both, ensure they are very gentle and used on separate days. For instance, a very mild enzyme mask once a week and a chemical exfoliant twice a week might work for some, but proceed with extreme caution.
Yes, but it requires a very gentle approach. Sensitive skin benefits from exfoliation as it helps remove dullness and improve product absorption. Opt for mild chemical exfoliants like lactic acid or mandelic acid, or gentle enzymatic exfoliants. Avoid harsh physical scrubs completely, and always patch test new products.
Key signs include increased redness, irritation, stinging or burning sensations, excessive dryness, flakiness, tightness, and sometimes even new breakouts or rashes. If you observe these symptoms, stop exfoliating immediately and focus on repairing your skin barrier with soothing, hydrating products.
Absolutely yes. Exfoliation removes the top layer of dead skin cells, revealing newer, more vulnerable skin beneath. This new skin is more susceptible to sun damage. Always apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days or when indoors.
Conclusion
Navigating the world of exfoliation can seem daunting given the array of choices, but with a clear understanding of your skin’s unique needs and the distinct benefits of each method, achieving a luminous, healthy complexion is entirely within reach. Whether you opt for the immediate satisfaction of physical exfoliation or the gentle, deep action of chemical exfoliants, the ultimate goal remains the same: to promote your skin’s natural renewal, allowing its inherent radiance to shine through. Remember, the journey to exceptional skin is less about rigid rules and more about thoughtful choices, consistent care, and a gentle responsiveness to what your skin truly needs.





